728x90
반응형
탐색(Search) 알고리즘 개요
탐색은 주어진 데이터에서 원하는 값을 찾는 과정을 의미합니다.
| 알고리즘 | 특징 |
| 완전 탐색(Brute Force) | 모든 경우를 하나씩 확인 |
| 이진 탐색(Binary Search) | 정렬된 배열에서 반씩 줄여가며 탐색 |
| 백트래킹(Backtracking) | 재귀적으로 경우의 수를 탐색하며 불가능한 경로는 가지치기 |
1. 완전 탐색(Brute Force)
- 가능한 모든 경우를 직접 확인하여 답을 찾는 방법
- 효율적이지 않지만, 작은 데이터에서는 단순하고 직관적
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
int main() {
vector<int> arr = {3, 1, 4, 1, 5, 9};
int target = 4;
bool found = false;
for (int num : arr) {
if (num == target) {
found = true;
break;
}
}
cout << (found ? "찾았다!" : "없다!") << endl;
return 0;
}2. 이진 탐색(Binary Search)
- 정렬된 배열에서 탐색을 빠르게 수행하는 알고리즘
- 중앙값을 기준으로 절반씩 줄여가며 탐색
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
bool binarySearch(vector<int>& arr, int target) {
int left = 0;
int right = arr.size() - 1;
while (left <= right) {
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return true;
}
else if (arr[mid] < target) {
left = mid + 1;
}
else {
right = mid - 1;
}
}
return false;
}
bool binarySearchRecursive(vector<int>& arr, int left, int right, int target) {
if (left > right) {
return false;
}
int mid = left + (right - left) / 2;
if (arr[mid] == target) {
return true;
}
if (arr[mid] < target) {
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, mid + 1, right, target);
}
return binarySearchRecursive(arr, left, mid - 1, target);
}
int main() {
vector<int> arr = { 1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11 }; // 정렬된 배열
cout << (binarySearch(arr, 5) ? "찾았다!" : "없다!") << endl;
cout << (binarySearchRecursive(arr, 0, arr.size() - 1, 5) ? "찾았다!" : "없다!") << endl;
return 0;
}3. 백트래킹(Backtracking)
- 모든 경우의 수를 탐색하지만, 불가능한 경로는 가지치기
- 주로 조합, 순열, 그래프 탐색 등에 사용
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
void backtrack(vector<int>& nums, vector<bool>& used, vector<int>& current) {
if (current.size() == nums.size()) {
for (int num : current) {
cout << num << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < nums.size(); i++) {
if (!used[i]) {
used[i] = true;
current.push_back(nums[i]);
backtrack(nums, used, current);
current.pop_back();
used[i] = false;
}
}
}
int main() {
vector<int> nums = { 1, 2, 3 };
vector<bool> used(nums.size(), false);
vector<int> current;
backtrack(nums, used, current);
return 0;
}그래프 탐색(Graph Traversal)
그래프 탐색은 노드(Node)와 간선(Edge)으로 이루어진 그래프에서 특정 노드들을 방문하는 과정입니다.
- V : 정점(Vertex)의 개수
- E : 간선(Edge)의 개수
| 알고리즘 | 탐색 방식 | 사용 구조 | 시간 복잡도 |
| DFS(깊이 우선 탐색) | 깊이(하위 노드)부터 탐색 | 재귀(스택) | O(V+E) |
| BFS(너비 우선 탐색) | 가까운 노드부터 탐색 | 큐 | O(V+E) |
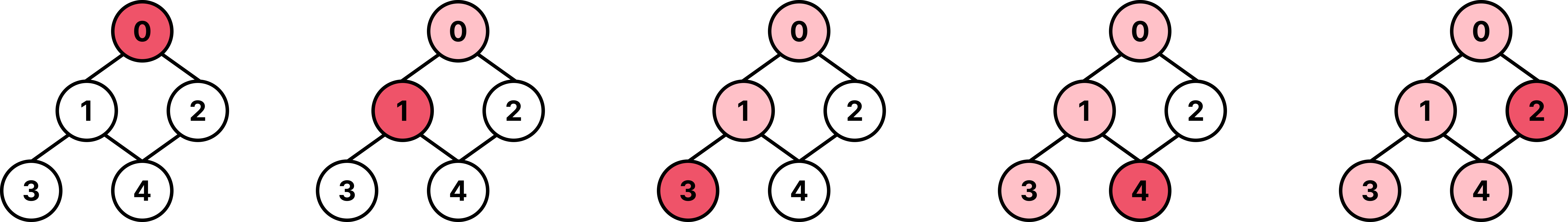
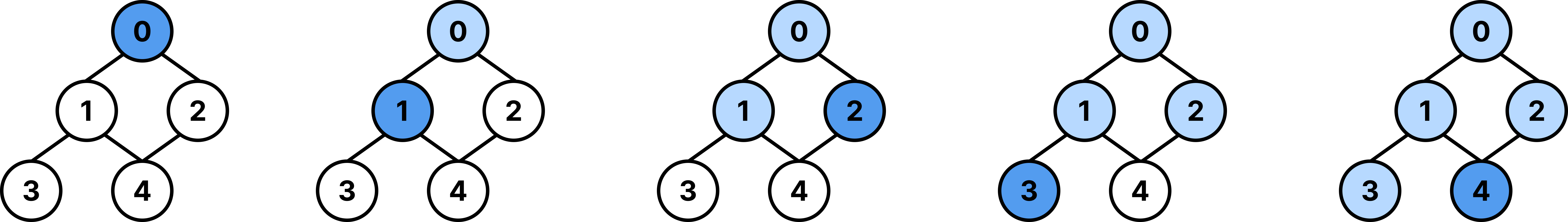
1. DFS(Depth-First Search, 깊이 우선 탐색)
- 한 방향으로 최대한 깊이 탐색 후, 다시 돌아와 다른 경로 탐색
- 스택이나 재귀를 이용해서 구현 가능
탐색 흐름
- 0 방문 ➡️ 1 방문 ➡️ 3 방문 (더 깊이 갈 곳 없음, 1로 되돌아감)
- 4 방문 (더 깊이 갈 곳 없음, 1로 되돌아감 ➡️ 더 깊이 갈 곳 없음, 0으로 되돌아감)
- 2 방문 ➡️ 4는 이미 방문됨 (종료)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
vector<bool> visited;
void dfs(int node) {
visited[node] = true;
cout << node << " ";
for (int next : graph[node]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
dfs(next);
}
}
}
int main() {
int V = 5; // 노드 개수
graph.resize(V);
visited.resize(V, false);
// 그래프 생성 (0-1, 0-2, 1-3, 1-4, 2-4)
graph[0] = { 1, 2 };
graph[1] = { 0, 3, 4 };
graph[2] = { 0, 4 };
graph[3] = { 1 };
graph[4] = { 1, 2 };
cout << "DFS 탐색 순서: ";
dfs(0); // 0 1 3 4 2
return 0;
}2. BFS(Breadth-First Search, 너비 우선 탐색)
- 가까운 노드부터 탐색
- 최단 경로 문제에 자주 사용됨
탐색 흐름
- 0 방문 ➡️ 1, 2 큐에 추가
- 큐에 있는 1 방문 ➡️ 3, 4 큐에 추가
- 큐에 있는 2 방문 ➡️ 4는 이미 추가됨
- 큐에 있는 3 방문 (더 탐색할 곳 없음)
- 큐에 있는 4 방문 (더 탐색할 곳 없음)
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
using namespace std;
vector<vector<int>> graph;
vector<bool> visited;
void bfs(int start) {
queue<int> q;
q.push(start);
visited[start] = true;
while (!q.empty()) {
int node = q.front();
q.pop();
cout << node << " ";
for (int next : graph[node]) {
if (!visited[next]) {
visited[next] = true;
q.push(next);
}
}
}
}
int main() {
int V = 5; // 노드 개수
graph.resize(V);
visited.resize(V, false);
// 그래프 생성 (0-1, 0-2, 1-3, 1-4, 2-4)
graph[0] = { 1, 2 };
graph[1] = { 0, 3, 4 };
graph[2] = { 0, 4 };
graph[3] = { 1 };
graph[4] = { 1, 2 };
cout << "BFS 탐색 순서: ";
bfs(0); // 0 1 2 3 4
return 0;
}728x90
반응형
'개발 > 알고리즘' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 그래프(Graph) (0) | 2025.05.02 |
|---|---|
| 정렬(Sorting) (0) | 2025.03.17 |